Capture a Mosaic
A mosaic is a visual image of your sample surface. The camera captures a series of small, high-resolution images and stitches them together into a single mosaic, giving you a large image of the sample surface that you can use for your analysis. The mosaic acts as a workspace for your analysis, where you can explore regions of interest and specify areas and points for your IR data collection.
In general, when you are analyzing a sample, you will collect a low-magnification mosaic image with a 4x or 10x objective, adjust your settings as needed, then if needed, capture a high-magnification mosaic of a smaller area using the 15x or 30x objective. When you have captured a mosaic, draw regions or select particles, and begin measuring data.
You can capture a mosaic automatically when you start the session or manually from the Session view.
Types of mosaics
There are two types of mosaics:
- Low-magnification (4x or 10x). Begin your analysis by capturing a low-magnification mosaic. This provides a larger overview of the sample surface.
- High-magnification (15x or 30x). If needed, capture a high-magnification mosaic of a smaller area of interest. The highmagnification mosaic provides a better image but takes longer to collect.
Automatic and manual captures
You can capture a mosaic automatically when you begin your session or you can first refine your measurement settings and then capture the mosaic manually.
Low-magnification mosaic
❖ To capture a mosaic automatically
- From the dashboard, select an option from the Mosaic Capture list. If you pick any option other than "Custom Mosaic," the software captures the mosaic automatically when you begin the session.
- Typically, you should select Autofocus before capture before you begin your session. With this option selected, the software automatically brings the sample into focus and optimizes the lighting for the best mosaic.
- Select Start Session. The session begins and the software automatically captures the mosaic.
❖ To capture a mosaic manually
- If you have not started a session, on the dashboard, select Custom Mosaic from the Mosaic capture list. Then, click Start Session.
- In the Session view, use the Camera View and move the stage to the desired position.
- Make sure the lower-magnification objective is selected.
- Click Capture Mosaic.
High-magnification mosaics
You must capture a low-magnification mosaic before you can capture a high-magnification mosaic.
❖ To capture a high-magnification mosaic
- In the session view, select the Mosaic tool from the floating toolbar.
- Click and drag to draw a rectangle on the low-magnification mosaic. This is the area where the high-magnification mosaic will be captured.
- Click Change Objective to select the high-magnification option (usually 15x), if it is not already selected.
- Select Capture Mosaic. The high-magnification mosaic is drawn on the top of the previous mosaic and a thumbnail image is added to the mosaic tab of the results panel.
Snapshots
A snapshot is a single image of the sample surface as it is viewed from the camera view.
❖ To capture a snapshot
- In the session view, open the Camera View.
- Click the snapshot tool. The snapshot is added to the mosaics tab.
Exploring mosaics
Use the navigation tools to zoom in or out and to view different areas of the mosaic.
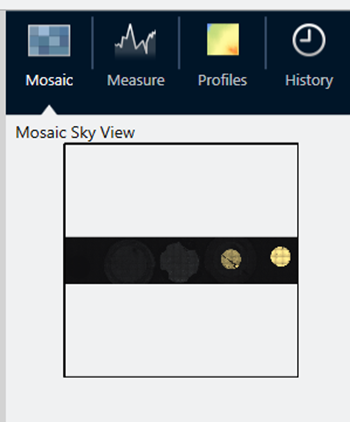
The mosaic sky view
The sky view displays a high-level image of the mosaic. When you zoom in to view the mosaic, the sky view shows you where you are looking on the sample surface.
You can also use the sky view to navigate the mosaic. Click an area on the sky view to move to that location. Click and drag the border of the focused region to zoom in or out.
Navigation tools
-
To zoom in and out
- Use the mouse scroll wheel to zoom in and out on the mosaic.
- Once you have zoomed in slightly, you can use the mosaic sky view to zoom. Click and drag the border of the focused region on the sky view to make it larger or smaller.
-
To view different areas of the mosaic, select the pan tool. With the pan tool selected, click and drag to move the mosaic image.


