Settings for FT-Raman measurements
Set the Raman module as your sampling location to view relevant settings and to start your FT-Raman session. Select More to view even more settings.
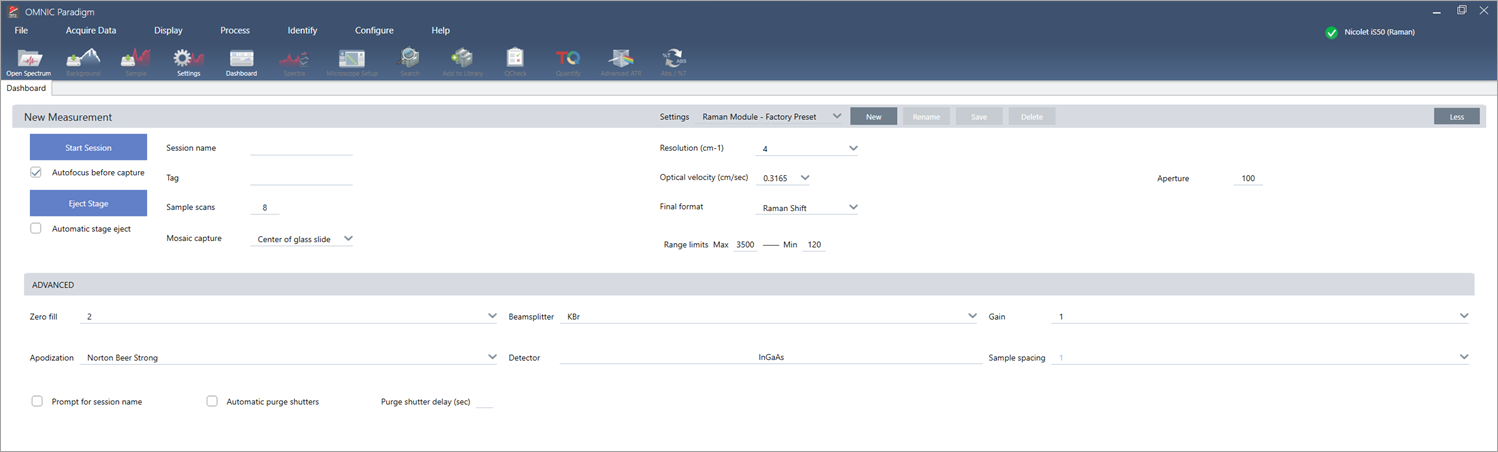
|
Setting |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Autofocus before capture |
Select to automatically bring the sample into focus when starting the session. |
|
Session name |
The name of the session data. This name is used in the saved data and, if you have Security Suite software installed, in the audit trail. The default name is the date and time the session was started. |
|
Tag |
Add a tag to the session. Tags are useful for finding and filtering your saved sessions later. |
|
Sample scans |
The number of scans collected at each sample point. Fewer scans results in faster data collection but potentially noisier data. |
|
Mosaic capture |
Specify a mosaic type to capture automatically when you start the session. To start the session without capturing a mosaic, select Custom Mosaic. Extremely large mosaics require a large amount of hard-drive space to store and are time consuming to collect. To save disk space and measurement time, capture a mosaic of only the portion of the sample that you need for your analysis. |
|
Resolution (cm-1) |
Like the resolution of a photo or video, a better resolution will mean finer detail in your spectral data. For example, a better resolution will distinguish between two very close peaks while a poor resolution might combine them. A smaller value results in a better resolution but also takes longer to measure. |
|
Optical velocity |
Determines the optical velocity in the interferometer. The default value is determined by the type of detector you are using, and can only be changed on certain spectrometers. |
|
Final format |
Select how the measured data is displayed. The options are Raman shift or Interferogram. |
|
Range limits |
Sets the limits for the range of frequencies, in wavenumber, included in the collected spectrum. |
|
Aperture |
Controls the intensity of the infrared radiation that reaches the sample. Aperture can only be changed when using spectrometers with adjustable apertures. In general, larger apertures will result in a better signal-to-noise ratio while smaller apertures result in better stability and accuracy. Small apertures are better for high-resolution measurements. You may need to use small apertures to acquire true high-resolution spectra. |
|
Zero fill |
Interpolates data points between the collected data points. This doesn’t increase the actual resolution of the data, but can smooth out sharp features and improve the line shape of a spectrum. Collect your sample and background spectra using the same Zero Fill setting. Options
|
|
Beamsplitter |
Select a beamsplitter. |
|
Gain |
Sets the amplification of the detector signal. Higher gain increases the signal but also increase the noise. The optimal gain depends on the experiment. |
|
Apodization |
Apodization refers to a mathematical function that is applied to the interferogram to reduce or remove peak side-lobes that can occur because the interferogram is not an infinite set of data. Strong apodization reduces more noise but can also reduce the resolution of the data and broaden peaks. See "Apodization Functions" for a description of each of the options. |
|
Detector |
Select the detector in use. |
|
Sample spacing |
Sample spacing refers to how frequently the interferogram is sampled. Lower sample spacing settings allow you to measure a more extended frequency range, and higher sample spacing settings are useful when measuring with very fast optical velocities, when the mirror is moving too quickly for the IR measurement to keep up.
|
|
Prompt for session name |
If selected, the software presents a prompt to enter a new session name at the beginning of every new session. |
|
Automatic purge shutters |
Select to enable the automatic purge shutters. |
|
Purge shutter delay (sec) |
Set a duration for the purge shutter delay in seconds. |

